Operation Market Garden (Part 2)
Field Marshal Montgomery's goal was to force an entry into Germany over the Lower Rhine. He wanted to circumvent the northern end of the Siegfried Line and this required the operation to seize the bridges across the Maas (Meuse) River and two arms of the Rhine (the Waal and the Lower Rhine) as well as several smaller canals and tributaries. Crossing the Lower Rhine would allow the Allies to encircle Germany's industrial heartland in the Ruhr from the north. It made large-scale use of airborne forces, whose tactical objectives were to secure the bridges and allow a rapid advance by armored units into Northern Germany.

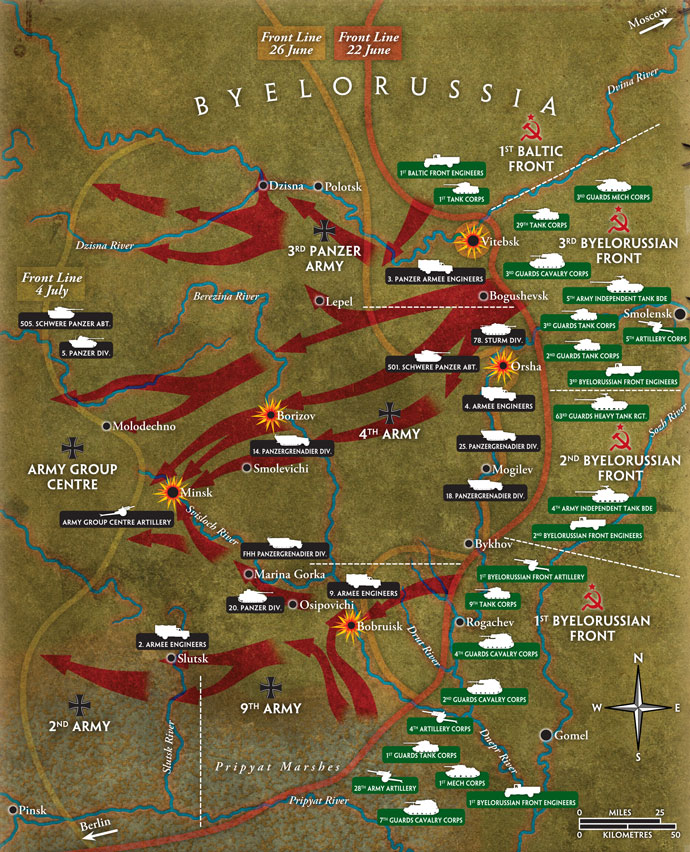
Several bridges between Eindhoven and Nijmegen were captured at the beginning of the operation but Gen. Horrocks' XXX Corps ground force advance was delayed by the demolition of a bridge over the Wilhelmina Canal. This caused an extremely overstretched supply line, and failing to capture the main road bridge over the river Waal before 20 September.
The Allied Airborne Army comprised of four divisions; two British and two American. Linked to it was the Polish Independent Parachute Brigade lead by Major-General Sosabowski.
The two most senior American commanders were Major-General Gavin of the 101st Division and Major-General Maxwell Taylor of the 82nd Division. Both men were knowledgeable in airborne warfare. The British First Airborne Division was lead by Major-General Urquhart. He was an unusual choice to lead the Airborne Division as he had never parachuted before, never participated in a glider landing and got air sick. He, himself, expressed his surprise when he was appointed commander of the division.

Robert Urquhart
The First Airborne Division had not taken part in D-Day. It had been kept in reserve and had remained inactive after June 1944. A number of planned operations had been cancelled at the last minute because they were not needed due to the success of the British armoured columns on the ground. By September 1944, the First Division was "restless, frustrated and ready for anything". Urquhart said that it was:"Battle-hungry to a degree which only those who have commanded large forces of trained soldiers can fully comprehend."
The First Division was given the task of capturing the bridge at Arnhem and holding it. The 101st Division was to capture the Zuid Willems Vaart Canal at Veghel and the Wilhelmina Canal at Son. The 82nd Division was to capture the bridges at Grave and at Nijmegen.
The attack had to be planned in just six days. Urquhart's First Division faced two major problems; the shortage of aircraft and the belief that the bridge at Arnhem was surrounded by anti-aircraft guns that would make a landing by the bridge itself too difficult.
The Americans were given the priority with regards to aircraft. The capture of the bridge at Arnhem would be pointless if the Americans failed to captured their targets. Therefore, the Americans would be carried to their targets in one lift whereas the attack on Arnhem would be done in three separate lifts during the day. Any night time landings were considered too dangerous.
This posed a major problem for Urquhart. His first force would have the element of surprise and, if the German resistance was minimal, would hold the bridge and secure any landing zones for the gliders. However, any subsequent landings would be after the Germans would have had the time to get themselves organised.
Intelligence reports also showed that the flak around the bridge itself was heavy. This was confirmed by RAF bomber crews who encountered the flak on their regular flights into Germany. Urquhart decided to make his landings to the west away from the bridge even though he knew that this was a risk. If the German resistance was stronger than anticipated, there was the chance of the first landing not even getting to Arnhem Bridge and taking out the flak.
British Intelligence reports indicated that the German presence in Arnhem was minimal. It was believed that the Germans only had six infantry divisions in the area with 25 artillery guns and only 20 tanks. German troops, in an Intelligence report of September 11th, were said to be "disorderly and dispirited". A similar report was made on September 17th.
Arnhem, the Bridge too Far:
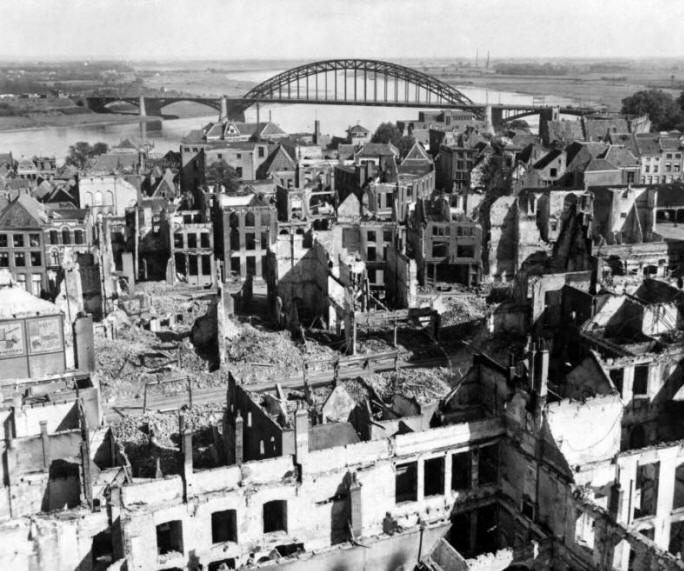

At Arnhem, the British 1st Airborne Division encountered far stronger resistance than anticipated. In the ensuing battle, only a small force managed to hold one end of the Arnhem road bridge and after the ground forces failed to relieve them, they were overrun on 21 September.
The rest of the division, trapped in a small pocket west of the bridge, had to be evacuated on 25 September. The Allies failed to cross the Rhine in sufficient force and the river remained a barrier to their advance until offensives at Remagen, Oppenheim, Rees and Wesel in March 1945. The failure of Market Garden ended Allied expectations of finishing the war by Christmas 1944.
Arnhem Timeline
| September 17th 1944 | Operation Market Garden began. The British landing near Arnhem is met by heavy German resistance. The American 82nd Division captured its targets at Waals but met heavy resistance at Nijmegen. |
| September 18th 1944 | A German counterattack stopped the Americans entering Nijmegen. The British landing zone near Arnhem was heavily attacked by Bittich's SS in an effort to stop further British landings. |
| September 19th 1944 | The leading elements of the British 30th Corps reached the Americans at Nijmegen but all efforts to break through to the British at Arnhem fail. |
| September 20th 1944 | The bridge at Nijmegen was captured by a combined US/UK assault. |
| September 21st 1944 | The British paratroopers defending the northern end of the bridge at Arnhem were heavily attacked. Those British troops who did not get through to Arnhem formed a defensive barrier west of Oosterbeek. |
| September 22nd 1944 | The advance of British tanks to relieve Arnhem was delayed as a result of German attacks. |
| September 23rd 1944 | Attempts by the Poles and troops of 30th Corps to cross the river at Arnhem failed. |
| September 25th 1944 | The surviving British troops were evacuated but nearly 3000 were captured. Over 1,200 British troops were killed in a plan that went a 'bridge too far.' |
Reports from the Dutch Resistance indicated beforehand that SS units had been seen in the Arnhem area. The First Airborne Division was only given this information on September 20th - three days after the attack on the bridge at Arnhem had begun.
Operation Market Garden began on Sunday morning, September 17th, 1944. Luftwaffe fighters bases had been attacked as had German barracks based near the drop zones. 1,000 American and British fighter planes gave cover as the gliders and their 'tugs' crossed the North Sea and headed over mainland Europe. The greatest fear was from flak and Intelligence estimated that the loss of gliders and transport craft could be up to 40%. As it was, very few of the 1,545 aircraft and 478 gliders were lost.
The 82nd Division landed without major problems around Grave and Nijmegen. The 101st Division was equally successful and by nightfall, the Americans and British armoured corps had met up in Eindhoven.

However, by the 18th September, fog had played its part. The glider and tug flights that were due to cross on the second day could not do so. This affected the 82nd Division in that Gavin had fewer men to attack the bridges at Waal, especially the road bridge that had held out for three days during the German attack on Holland in 1940. This bridge only fell in the evening of Wednesday 20th after a combined American/British attack. With this bridge captured, the 30th Corps armour could race towards Arnhem to relieve Urquhart's First Airborne Division there.
At Arnhem, the British met much stiffer opposition than they had been lead to believe. The IX th and X th SS Panzer Divisions had re-grouped at Arnhem - as Dutch resistance had warned. Both groups comprised of 8,500 men lead by General Willi Bittrich.
These were not the poorly equipped German garrison troops, low in morale, that British Intelligence had claimed were stationed at Arnhem. Bittrich - a highly regarded general in the Waffen SS - sent in the IX SS Division to the British landing zones immediately. The X Division was ordered to Nijmegen to stop the 2nd Army group advancing on Arnhem. Bittrich was confident of success:
"We shall soon be able to discount the threat of the British north of the Neder Rijn. We must remember that British soldiers do not act on their own initiative when they are fighting in a town and when it consequently becomes difficult for officers to exercise control. They are amazing in defense, but we need not be afraid of their capabilities in attack." - Bittrich.
The men from the IX th Division quickly created a formidable defensive line to stop the British advancing to Arnhem. The British faced a number of serious problems in the landing zone. Nearly all the vehicles used by the Airborne Reconnaissance Squadron were lost when the gliders carrying them failed to land. Therefore the advance into Arnhem itself was delayed but also had to be done almost entirely on foot. The job of the Reconnaissance Squadron was to move off in jeeps etc. in advance and secure bridges and roads. This they could not do after the loss of their vehicles. The maps issued to officers also proved to be less than accurate.
The British paratroopers quickly came under German fire. Only the 2nd Battalion lead by Lt. Col. Frost moved forward with relative ease but even they were occasionally halted by German fire. Frost's men were the most southerly of the British units and the Germans had covered their route to Arnhem less well than the other routes the British were to use.
When Frost got to the bridge at Arnhem, he only had about 500 men. He secured the northern end of the bridge and the buildings around it but he remained heavily exposed to a German attack across the bridge as the British had failed to secure the southern end of the bridge. Around Arnhem, British troops, engaged in combat with the SS, took heavy casualties. By now, the Germans were being reinforced with SS crewed Panzer VI Tiger tanks.
Despite being short of ammunition and with no food or water, Frost's men continued fighting.
A German who fought in the final battle for the bridge wrote:
"(The fighting was) an indescribable fanaticism...and the fight raged through ceilings and staircases. hand grenades flew in every direction. Each house had to be taken this way. Some of the British offered resistance to their last breath."
The 2nd Army failed to reach Arnhem. In the final drive - just 10 miles - from where the 2nd Army was to Arnhem, the SS fought with great skill seriously delaying the forward momentum that the 2nd Army had previously developed. Those British troops who remained in the Arnhem area were caught in land that the SS called 'The Cauldron'. A decision was made to withdraw. Those soldiers that could be evacuated were but many wounded were left behind.

In all, over 1,200 British soldiers had been killed and nearly 3,000 had been taken prisoner. 3,400 German troops had been killed or wounded in the battle.
Why did the plan fail?
- The speed with which Bittrich organised his men and his tactical awareness were major reasons for the German victory. British Intelligence had ignored Dutch Resistance reports that SS units were in the region. This was a fatal mistake.
- When the paratroops landed they found that their maps were inaccurate regarding the layout of the roads in the Arnhem area.
- Another major problem was that the radio sets issued to the men only had a range of 3 miles and thus proved to be useless when the various segments of the British army in the area were spread over 8 miles. Lack of communication proved a major handicap for commanders on the ground who rarely knew what other commanders were doing or planning.
- Landing was also planned to be spread over three days, The 1st Airborne Division was never up to full strength, and the element of surprise was lost